Aspherical lenses play a crucial role in modern optical systems. These lenses differ from traditional spherical lenses by avoiding optical aberrations. This improvement enhances image quality significantly. According to a report by Market Research Future, the global aspherical lens market is expected to reach $2 billion by 2025, indicating their growing importance in various applications.
Dr. James Monroe, an industry expert, states, "Aspherical lenses provide superior performance that traditional lenses simply cannot match." This highlights how professionals recognize the advantages offered by these innovative designs. However, the manufacturing of aspherical lenses can be complex and costly. Many companies face challenges when trying to incorporate them into their products.
Despite their benefits, not every optical system can justify the expense of aspherical lenses. There is a need for a careful evaluation of design specifications and cost-effectiveness. While the optical industry is evolving, it's essential to reflect on these hurdles. Balancing performance benefits with production challenges remains vital for future advancements in optical technology.

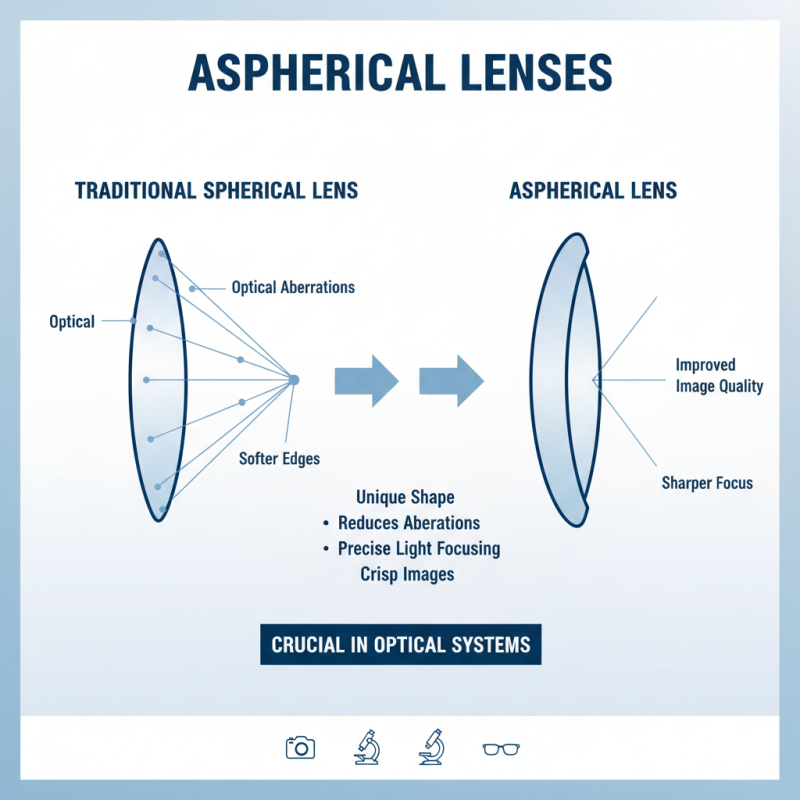
Aspherical lenses have unique shapes that differ from traditional spherical lenses. Their surfaces are crafted to reduce optical aberrations. This design improves image quality, making them crucial in various optical systems. They help in focusing light more precisely. This results in sharper images, especially at the edges.
One key characteristic of aspherical lenses is their versatility. They can be used in cameras, telescopes, and even in eyeglasses. This broad usage demonstrates their ability to enhance visual experiences. However, they can be more challenging to manufacture than standard lenses. This complexity can sometimes lead to production inconsistencies.
Tips: When choosing a lens, consider its shape and material. Different applications may require specific lens features. Remember, not all aspherical lenses perform alike. Test and compare options before making a decision. Ensuring quality can be a reflection of your needs.
When comparing aspherical and spherical lenses, the differences become clear. Spherical lenses are simpler, with a uniform curvature. This can create distortions and aberrations, especially in wide-angle applications. Their design is easy to manufacture and typically results in lower costs. However, they often struggle with achieving sharp focus across the entire image.
Aspherical lenses have a more complex shape. They can eliminate many optical aberrations, providing improved image quality. Their design allows for more control over the light paths. This leads to clearer, more detailed images. Yet, producing aspherical lenses is often more challenging. It requires advanced techniques and precision manufacturing. This complexity can lead to higher prices, but the benefits may justify the cost.
The differences affect applications significantly. In photography, for instance, aspherical lenses can bring out finer details. Spherical lenses may fall short when users push their limits. Consider the trade-offs carefully. The choice between these lenses impacts both performance and budget. Opting for a lens involves real choices that show the balance between quality and cost.
This chart illustrates the light transmission efficiency of aspherical lenses compared to spherical lenses. As shown, aspherical lenses provide a higher efficiency of 95%, while spherical lenses offer 85%. This difference highlights the advantages of aspherical lenses in optimizing optical performance.
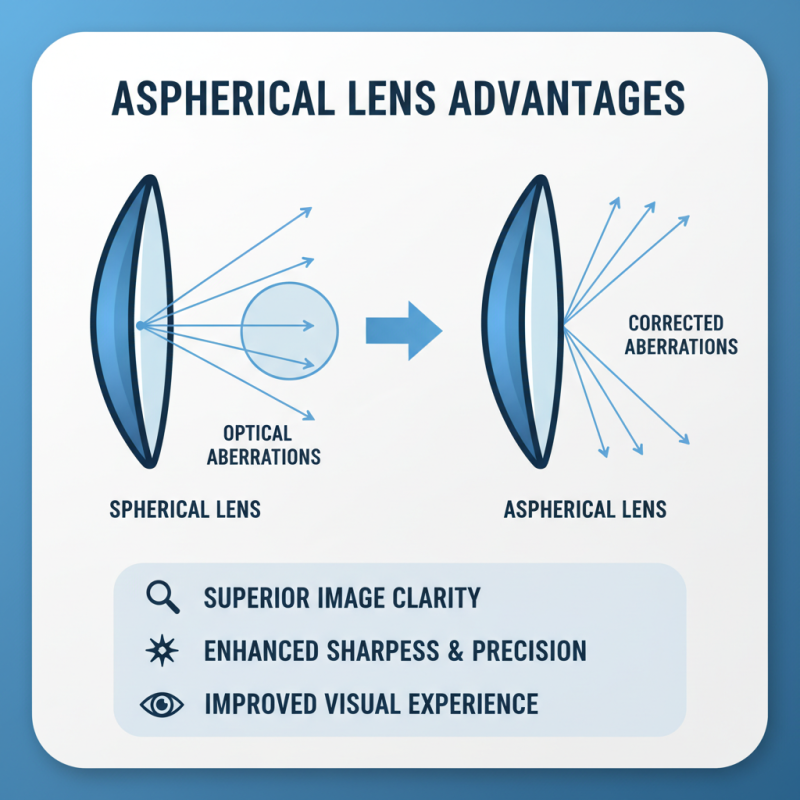
Aspherical lenses have distinct advantages in optical systems. Unlike traditional spherical lenses, they are designed with a more complex shape. This design helps correct optical aberrations more effectively. The result is clearer images with increased sharpness and precision. Users often appreciate the improvements in image quality.
One significant benefit of aspherical lenses is their ability to reduce the size and weight of optical devices. These lenses allow for thinner and lighter designs, which is essential in portable equipment. Compact systems often perform better in practical uses. Additionally, aspherical lenses contribute to wider fields of view. They help capture more of the scene in a single frame.
Despite their advantages, aspherical lenses can be challenging to manufacture. Achieving the precise shape can lead to higher production costs. Some users may find the quality inconsistent at times. These imperfections are worth considering when evaluating aspherical lenses. However, the benefits often outweigh the drawbacks for many applications, making them an attractive option in advanced optical systems.
Aspherical lenses play a vital role across various industries. Their unique shapes reduce optical aberrations, enhancing image quality. This is crucial in photography, where clarity matters. According to a recent market report, the aspherical lens market is projected to grow by over 15% annually. This growth indicates increased adoption in cameras and mobile devices, emphasizing performance.
In the automotive industry, aspherical lenses are used in headlight systems. They create brighter, more focused beams. A study showed that using aspherical lenses improved visibility by up to 30%. This improvement can lead to safer driving experiences, especially at night. However, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly. Some companies struggle with production consistency and quality control.
Medical imaging also benefits from aspherical lens technology. These lenses enhance the resolution of imaging devices, allowing for better diagnostics. Reports suggest that radiology departments investing in high-quality aspherical lenses report a 20% increase in diagnostic accuracy. Despite these advantages, the integration of such lenses can pose challenges. The transition often requires extensive retraining for staff.
| Dimension | Description | Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape | Non-spherical surface that improves optical performance | Reduces optical aberrations, enhances image quality | Cameras, projectors, and microscopes |
| Material | Made from various optical materials like glass and plastics | Lightweight and versatile for different applications | Consumer electronics, telecommunications |
| Design Complexity | Complex geometries designed using advanced software | Customizable to specific optical requirements | Medical devices, laser systems |
| Cost-effectiveness | Higher initial manufacturing cost for intricate designs | Long-term savings due to enhanced performance | Aerospace, optical instruments |
Aspherical lenses have become essential in modern optical systems. Their unique shapes help reduce optical aberrations. However, designing these lenses presents distinct challenges. Creating precise curves is complex and requires advanced technology. This can lead to increased production costs, with recent reports indicating that aspherical lens manufacturing costs can be up to 30% higher than traditional lenses.
Another consideration is the material selection. Common materials such as glass and plastics each have pros and cons. For instance, while glass provides superior optical clarity, it is heavier and more fragile. On the other hand, plastics are lighter and more impact-resistant but may not match the same optical quality. This poses a dilemma: how to balance weight, durability, and optical performance.
Finally, lens shape variability is a crucial issue. Each application may demand custom designs, leading to longer lead times. Some designs might not achieve the desired outcomes, requiring iterations. The pursuit of perfect aspherical shapes demands continuous refinement and testing. This ongoing process highlights the need for flexibility in design, as well as the significance of research and development in this field.







