A Resin Lens is gaining popularity in various fields, particularly in optics. These lenses are made from synthetic materials that can offer flexibility and durability. Unlike traditional glass lenses, resin lenses are lighter and often shatter-resistant. This makes them ideal for eyewear, cameras, and other optical devices.
Understanding how a Resin Lens works reveals its advantages. The process of creating these lenses involves careful manipulation of materials. Different types of resin can be mixed to achieve specific optical properties. This aspect, however, can also lead to inconsistencies in quality, requiring manufacturers to pay close attention.
Resin lenses provide excellent clarity and can be coated for added protection. However, not all resin lenses are created equal. Some may scratch easily or suffer from distortion. Users must consider the trade-offs when choosing a lens. The balance between cost, quality, and performance is crucial.
Resin lenses have gained popularity in the optical industry due to their lightweight properties and scratch resistance. They are crafted from a type of plastic, making them an attractive option for various applications. Common types include polycarbonate and CR-39 lenses. According to industry reports, polycarbonate lenses account for around 40% of the eyewear market, mainly due to their impact resistance. These lenses are also 20% lighter than traditional glass lenses.
In terms of function, resin lenses bend light to provide clear vision. Their ability to be molded into various shapes allows for diverse designs. However, these lenses are not without flaws. Some users report distortion at the edges, a common issue with certain lens types. The refractive index can impact clarity, making it important to choose wisely. Research indicates that 15% of users experience dissatisfaction due to lens quality.
Choosing the right type of resin lens requires careful consideration. The cost-effectiveness of such lenses often leads to compromises in quality. Only 30% of consumers prioritize lens coatings, which can enhance durability. Understanding the differences between types, such as UV protection or anti-reflective coatings, is essential. This knowledge influences both comfort and performance, impacting overall user experience.
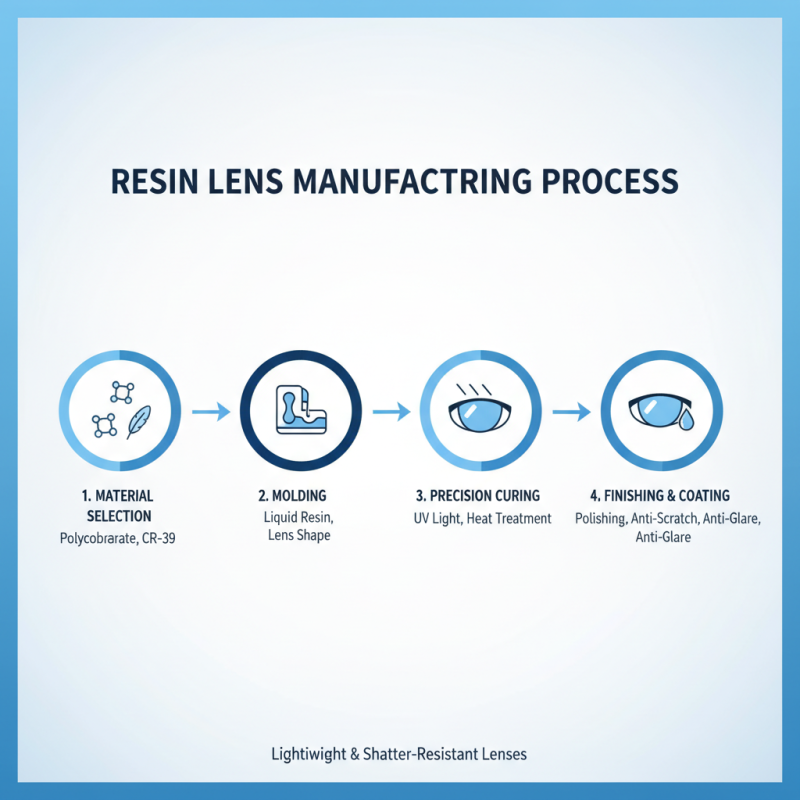
The manufacturing process of resin lenses involves several crucial steps. First, raw materials like polycarbonate or CR-39 are selected. These materials are favored for their lightweight and shatter-resistant properties. They can be molded into different shapes. This stage requires careful precision to ensure clarity and durability.
Next, the resin is heated and poured into molds to form the lens shapes. During this process, bubbles can often form. This can lead to imperfections in the final product. Manufacturers must monitor temperature and mixing carefully. After molding, the lenses are polished. This helps achieve the desired optical clarity. However, polishing can sometimes wear down edges, causing a need for further adjustments.
Once polished, the lenses undergo surface treatments. These treatments can include anti-reflective coatings or scratch-resistant layers. Yet, achieving the right balance can be tricky. Some lenses may end up too thick or heavy. Troubleshooting these issues is vital for quality. Finally, inspection ensures each lens meets standards, but human error can still play a role. The entire process reflects a blend of art and science, with room for improvement at every stage.
Resin lenses have gained popularity due to their lightweight properties and impact resistance. According to a report by the Optical Laboratories Association, nearly 85% of lenses produced today are made from polymer materials like resin. This shift indicates a growing preference for resin over traditional glass. One major advantage of resin lenses is their durability. They are less prone to shattering, making them safer for active lifestyles.
However, resin lenses also have drawbacks. They can be more prone to scratches than glass lenses. A study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology shows that scratched surfaces impact vision clarity. In this regard, proper care is essential. Additionally, resin lenses can distort images under certain conditions, especially in high prescriptions. This distortion is less common with glass lenses, which maintain optical integrity better.
In contrast, glass lenses offer superior optical quality. They provide excellent clarity and are less prone to warping. However, they are significantly heavier and more fragile. For some, this weight can be uncomfortable over extended wear. The choice between resin and glass often boils down to individual needs. It's a balance of safety, comfort, and visual clarity. Each type warrants consideration based on lifestyle and personal preference.
| Aspect | Resin Lenses | Glass Lenses |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Durability | Impact resistant | More prone to shatter |
| Clarity | Good optical clarity | Excellent optical clarity |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Usually more expensive |
| Scratch Resistance | Lower scratch resistance | Higher scratch resistance |
| UV Protection | Good UV protection available | Excellent UV protection |
| Applications | Commonly used in eyeglasses, safety goggles | Used in high-end eyewear, camera lenses |
Resin lenses have found their way into various industries due to their lightweight and durable nature. In eyewear, manufacturers favor resin lenses for their ability to withstand impacts. Reports indicate that nearly 70% of eyewear products now use resin materials. This shift not only enhances safety but also provides better comfort for users.
In the camera industry, resin lenses significantly impact image quality. Their ability to minimize chromatic aberration allows for clearer photographs. The demand for resin in this sector has increased by about 15% over the past year. Cameras equipped with resin lenses also tend to be more affordable, attracting hobbyists and professionals alike.
Tips: When selecting resin lenses, consider the thickness and coating options. Thicker lenses may be heavier but offer greater durability. Keep in mind that not all resin lenses are created equal; ask about the manufacturer's standards. Be cautious of misunderstandings around lens care, as improper cleaning can lead to scratches. Always use recommended cleaning solutions to extend the life of your lenses.
Resin lenses are popular in eyewear for their lightweight and shatter-resistant properties. They are made from a synthetic polymer, offering a comfortable fit. When it comes to optical clarity, resin lenses provide decent vision. However, they can scratch easily if not cared for properly.
The performance data of resin lenses shows a good balance of attributes. Their refractive index typically ranges from 1.50 to 1.60. This means they can bend light effectively, providing clear vision. Yet, higher refractive lenses may have issues with distortion. The protective coatings applied to resin lenses can enhance scratch resistance, but they may wear off over time.
Some users report that resin lenses can create glare in bright sunlight. While UV protection is often included, it's not perfect. It’s essential to wear proper sunglasses outdoors. Getting accustomed to resin lenses may take time. Some wearers experience discomfort initially. Adjustments might be necessary for an optimal fit.







